How Many People Are Born Every Second? This captivating question takes us on an extraordinary journey, unveiling the intricacies of global birth rates. From the bustling streets of Asia to the sprawling landscapes of Africa, we’ll explore the factors shaping this fundamental aspect of human existence.
Delving into regional variations, we’ll uncover the cultural, social, and economic forces that influence birth rates across continents. We’ll trace historical trends, examining how wars, famines, and medical advancements have left their mark on human reproduction.
Global Birth Rate
The global birth rate refers to the number of live births occurring per second worldwide. It is a key indicator of population growth and dynamics, influenced by various factors such as access to healthcare, education, and economic conditions.
Factors Influencing Global Birth Rate
Multiple factors contribute to the global birth rate, including:
- Access to Healthcare:Improved healthcare services, including prenatal care, delivery assistance, and family planning, can lead to lower birth rates as women have greater control over their reproductive choices.
- Education:Education, particularly for girls, empowers individuals with knowledge about reproductive health and family planning, contributing to lower birth rates.
- Economic Conditions:Economic stability and prosperity can positively impact birth rates as families have better access to resources, education, and healthcare, leading to more informed reproductive decisions.
Regional Variations
The birth rate varies significantly across different regions of the world, influenced by a complex interplay of factors such as cultural norms, social policies, and economic development.
Birth Rates in Different Regions
| Region | Birth Rate (per 1,000 population) |
|---|---|
| Asia | 18.4 |
| Africa | 24.1 |
| Europe | 10.5 |
| Americas | 16.3 |
Factors Influencing Regional Variations
Cultural Norms:Cultural values and beliefs play a significant role in shaping birth rates. For example, in some cultures, large families are highly valued, while in others, smaller families are preferred.
In the grand tapestry of life, the constant rhythm of birth continues, with an estimated 4.4 people entering the world every second. Amidst this vibrant tapestry, it is equally crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of those already here.
As stipulated in Under The Occupational Health And Safety Act , employers have a fundamental responsibility to safeguard their employees’ health and safety. By prioritizing workplace well-being, we not only protect the individuals within but also contribute to a thriving and sustainable society where the relentless march of life continues unabated.
Social Policies:Government policies can also influence birth rates. Policies such as paid parental leave, childcare subsidies, and access to contraception can encourage or discourage childbearing.
Economic Development:Economic factors, such as income levels and employment opportunities, can impact birth rates. In general, higher levels of economic development are associated with lower birth rates.
Historical Trends
Birth rates have fluctuated throughout history, influenced by various factors. A timeline can illustrate these changes:
- Pre-Industrial Era:High birth rates due to limited contraception, high infant mortality, and reliance on agriculture.
- Industrial Revolution:Declining birth rates due to urbanization, industrialization, and improved living conditions.
- Early 20th Century:Birth rates stabilized or slightly increased due to medical advancements reducing infant mortality.
- Post-World War II:Baby boom in developed countries due to economic growth and social changes.
- 1970s-Present:Declining birth rates in developed countries due to factors such as urbanization, education, and career opportunities.
Impact of Events
Significant events have also impacted birth rates:
- Wars:Wars can lead to both increased and decreased birth rates, depending on the duration and intensity of the conflict.
- Famines:Famines can cause a sharp decline in birth rates due to malnutrition and disease.
- Medical Advancements:Improved healthcare and access to contraception have significantly reduced birth rates, especially in developed countries.
Demographic Implications
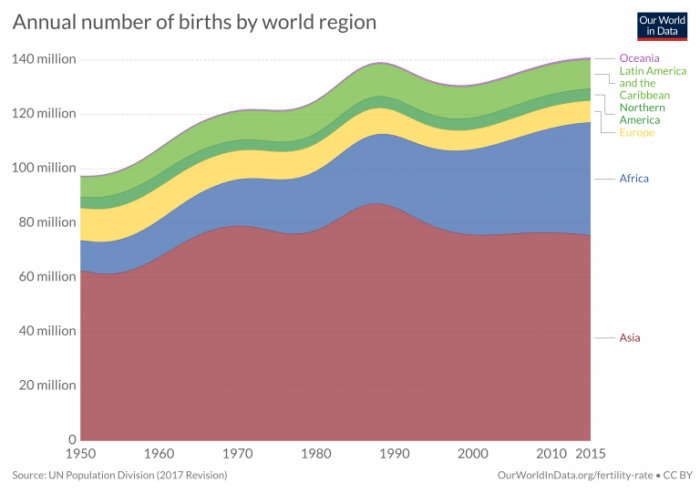
Birth rates have a significant impact on population growth and age distribution. Higher birth rates lead to a larger population, while lower birth rates can lead to population decline. The age distribution of a population is also affected by birth rates, as higher birth rates result in a larger proportion of younger people in the population.
Every second, around 4.3 new lives enter the world, a staggering statistic that underscores the miracle of life. As we marvel at this ceaseless cycle, let’s take a moment to appreciate the tranquility of nature along the Maribyrnong River Trail . This serene path meanders alongside the picturesque river, offering a respite from the hustle and bustle of life.
As we return to the topic at hand, we are reminded that with each passing second, the tapestry of humanity continues to be woven, a testament to the indomitable spirit of life.
Consequences of High or Low Birth Rates
High birth rates can lead to a number of potential consequences, including:
- Labor shortages: A large population of young people can lead to a shortage of workers in the labor force.
- Increased demand for resources: A larger population requires more resources, such as food, water, and housing.
- Environmental degradation: A larger population can put a strain on the environment, leading to increased pollution and deforestation.
Low birth rates can also lead to a number of potential consequences, including:
- Population decline: A low birth rate can lead to a decline in the population, which can have a negative impact on the economy and social services.
- Aging population: A low birth rate can lead to an aging population, which can put a strain on healthcare and pension systems.
- Reduced economic growth: A smaller population can lead to reduced economic growth, as there are fewer people to produce goods and services.
It is important to note that the consequences of high or low birth rates can vary depending on the specific context. For example, a high birth rate may be beneficial in a country with a rapidly growing economy, but it could be detrimental in a country with limited resources.
Similarly, a low birth rate may be beneficial in a country with a rapidly aging population, but it could be detrimental in a country with a young population.
Social and Economic Impacts
Birth rates profoundly influence societies and economies, shaping resource allocation, infrastructure demands, and societal structures.
Higher birth rates can strain educational systems, requiring more schools, teachers, and resources. In contrast, declining birth rates can lead to school closures and teacher layoffs. Healthcare systems also face challenges with fluctuating birth rates, as they must adapt to changing demands for prenatal care, pediatric services, and elderly care.
Education
- High birth rates can strain educational resources, leading to overcrowded classrooms and a shortage of qualified teachers.
- Declining birth rates can result in school closures and teacher layoffs, as schools struggle to maintain enrollment.
- Fluctuating birth rates can disrupt educational planning, making it challenging to allocate resources effectively.
Healthcare, How Many People Are Born Every Second
- High birth rates increase the demand for prenatal care, pediatric services, and childhood vaccinations.
- Declining birth rates can lead to a surplus of healthcare professionals specializing in pediatrics and obstetrics.
- Fluctuating birth rates can make it difficult for healthcare systems to plan for future needs.
Social Welfare
- High birth rates can increase the need for social welfare programs, such as childcare, housing assistance, and food stamps.
- Declining birth rates can reduce the demand for these programs, potentially leading to budget cuts.
- Fluctuating birth rates can create uncertainty in social welfare planning, making it difficult to meet the changing needs of society.
Economic Development
The relationship between birth rates and economic development is complex and varies depending on the context. In some cases, high birth rates can contribute to economic growth by increasing the labor force and stimulating demand for goods and services. However, in other cases, high birth rates can strain resources and lead to poverty and inequality.
Declining birth rates can also have economic implications. A shrinking labor force can lead to labor shortages and higher wages. However, it can also reduce the tax base and strain social welfare systems.
Future Projections
Predicting future birth rates is a complex task fraught with challenges. Nonetheless, demographers employ various models and consider historical trends, socioeconomic factors, and public policies to make informed projections.
Different scenarios emerge from these projections, each with its own set of implications for society and policymakers. These scenarios range from a continued decline in birth rates to a modest rebound or even a stabilization at current levels.
Declining Birth Rates
If birth rates continue to decline, societies may face challenges related to population aging, shrinking workforce, and strained social welfare systems. Governments may need to adjust retirement ages, increase immigration, or implement policies to encourage childbearing.
Modest Rebound
A modest rebound in birth rates could alleviate some of the challenges associated with population decline. However, it may not be sufficient to reverse the aging population trend. Governments may need to consider policies that support families and promote work-life balance.
Stabilization
If birth rates stabilize at current levels, societies may experience a more gradual transition to an aging population. This scenario may provide more time for governments to adapt their policies and prepare for the challenges ahead.
Ending Remarks: How Many People Are Born Every Second
As we contemplate the future, we’ll grapple with the challenges and opportunities of predicting birth rates. Different scenarios will be presented, each with its potential implications for society and policymakers.
Ultimately, our exploration of How Many People Are Born Every Second will shed light on the profound impact of birth rates on population growth, age distribution, and the very fabric of our societies.
Expert Answers
Why are birth rates declining in some regions?
Declining birth rates can be attributed to factors such as improved access to education and healthcare, urbanization, and changes in social norms.
How do birth rates affect the economy?
Birth rates can influence labor force size, economic growth, and the demand for goods and services.
What are the challenges of predicting future birth rates?
Predicting future birth rates is complex due to uncertainties in factors such as economic conditions, technological advancements, and social policies.